Меню:
Introduction
Currently we cannot pick out a content filtering into the dedicated branch of information security, so it mixed with other branches. For the information security, content filtering is very important, as it allow to detect an potentially dangerous things, and process them correctly. Approaches, that appears during development of products for content filtering, currently used for intrusion detection (IDS), detecting malicious code, and other negative actions.
On the base of new technologies and products for content filtering, are created an additional services for users, increased a quality of protection, and allowed not to only react to the existed threats, and to prevent a new, not known threats1.2
New trends in content filtering
One of the common trends in development of products for information security is tendency to implement different functions in one device or software product. Usually, developers try to create solutions, that besides the content filtering functions, also works as anti-viruses, firewalls and/or intrusion detection and prevention systems. From one side, this minimize costs for companies on purchasing and support of such solutions, but from other side — such products, often has restricted functionality. For example, in many products, functions for filtering of web-traffic are limited only to checking of URLs against some predefined database of URLs.
This trend is also applicable for development of products according the Unified Threat Management (UTM) concept, that provide unified approach to preventing different threats, not depending on what protocol or data is processed. This approach allow to avoid duplication of security functions, and also to provide an updated threat definitions for all parts of product.
In well known branches of content filtering — e-mail- and web-filtering, also occur a changes and appear new technologies. In e-mail filtering products, one of main function become a protection from phishing. And in web-filtering, focus is changing from using predefined URLs databases to on-line data categorisation, that is very actual when users works with different portal solutions.
Besides, this two well-known application of content filtering, also created a new branches — some time ago also was created products for control of instant messaging and peer-to-peer (p2p) communications. Currently, actively developed products for controlling of Voice over IP (VoIP) traffic.
In many countries, was started to actively develop products for the interception and analysis of the different kinds of information for the purpose of investigations (lawful interception). This happens at the government level and in most cases used for anti-terror investigations. Such systems, intercept and analyse not only data, transferred via computer networks, but also via usual communication channels — phones, radio-channels, etc. Most widely known intercept system is Echelon — the system, that was used by American agencies for the collecting different kinds of information. In Russia, also exists different implementations of the system for operative investigations (Russian abbreviation is SORM), that used by special agencies for intercepting and analysing information.
One of the main trends at the market of the content filtering products is very aggressive acquisitions. Although this trend has mostly organisational form, but this could lead to creation of new products and branches for companies, that had no such products, or their had a very little market place. We can illustrate this trend with following examples:
- Secure Computing Corporation, that had acquired Cyberguard company with number of good products for content filtering, in summer 2006 also had acquired the CipherTrust company, that provide many solutions for filtering e-mail and instant messaging;
- MailFrontier company, that had created different products for securing e-mail, was acquired by SonicWall, that hadn't at that time such products;
- in July 2006 SurfControl, well known by their content filtering solutions, had acquired the BlackSpider, that provide for customers managed security services;
- in August 2006, happens most vast acquisition — the Internet Security Systems (ISS) company had signed agreement with IBM about fusion. This fusion demonstrate very high interest to the information security branch from the big companies;
- In January 2007, Cisco had acquired IronPort, that had very good line of products for e-mail security;
- In September of 2006, Websense had acquired the Port Authority Technologies Inc, and enter to market of data leak prevention;
- Last years Microsoft had acquired different companies, that had worked in branch of computer & information security. Biggest of them was acquiring of Sybari with their anti-virus products, and also products for content filtering of mail and instant messaging.
I should to mention, that last time, also was created a open source products for content filtering. In many cases, their doesn't have same functional as commercial products, but exists a branches, where they successfully used.
Modern threats
Modern IT infrastructure work under pressure of many different type of attacks, targets for that are both ordinary users, and companies, independent on their size. Now, most actual threats are:
- Phishing — widespread threat, aimed in stealing important user information (passwords, credit card numbers, etc.). Usually this performed by sending special e-mail or IM messages, with URLs, that point to the fake sites, with the same design, as original;
- Spyware — different tools, that try to hijack control over your data, and/or your computer. There is different types of these tools, that differentiated by the degree of danger — from simple demonstration of ads, to logging of all data, that user enters, and hijacking control on computers work;
- Viruses, and other types of malware — well known treats for IT-infrastructure. But, every year, we got new types of malware, that often work via software vulnerabilities, that allow them propagate automatically;
- SPAM and SPIM — unwanted messages, that users get via e-mail (SPAM) or instant messaging (SPIM). This lead to additional time spending for handling these unwanted messages by users. Currently, as SPAM marked more than 70% of all e-mails;
- attacks on IT-infrastructure — IT-infrastructure of companies, is very important for work of entire company, and attacks aimed to stop it work, is very dangerous. Last time, very often used distributed attacks, that involve big networks of computers, infected by Trojan horses or other malware, that used to control work of computers;
- leakage of business information — prevention of such treats is one of the main tasks of content filtering products. Leakage of important information, could lead to very high loss, often comparable with loss of main funds. So, currently in many products, extending functions for detection of hidden channels of information leakage, such as steganography;
For first five threats targets are home and corporate computers. But, the last mostly applicable for companies.
Web-traffic filtering
Last years, in web-filtering branch, occur different changes, that influenced by creation of new filtering technologies, and changing in technologies, that are used for creating of web-sites.
One of the most important trends in the development of web-filtering products is transition from using of predefined URL databases, to categorisation of sites, based on their content. This is very actual for different portals, that can contain information from different categories, changing in time, and/or adopted to the client settings.
Expansion of popular technologies and tools for site building, such as Ajax, Macromedia Flash and others, require to add changes in the web-filtering technologies.
Usage of encrypted channels for access to Internet sites provide an additional shield of the transmitted data, but in the same time, they could be used as a channels for information leakage, or malware propagation.
Also actual problem of integrating security products with parts of IT-infrastructure, such as, proxy, web, mail and directory servers. Different companies and non-commercial organisations develop protocols for providing interoperability between different systems, listed above.
Description of current state of these questions is given below.
Approaches to web-sites & data categorisation
Web-sites categorisation could be performed by different ways. Currently we could distinguish following approaches to the categorisation:
- by using predefined site's databases with regular updates of site's lists and categories;
- by using on-line categorisation of site's content (we could use different methods for this task);
- by using categorisation information, provided by site.
Each of these methods has their own advantages and drawbacks.
Predefined URL databases
Usage of predefined URL databases, and all related things — well-known and used for a long time method. Now, such databases is provided by several companies, such as Websense, SurfControl, ISS/Cobion, Secure Computing, Astaro AG, NetStar and other. Some of these companies use this databases only in their own products, but several, allow to use them in third party products. Databases from Websense, Secure Computing, SurfControl and ISS/Cobion covers millions of sites in different languages, located in different countries, that is very actual in our time.
Sites categorisation and updating of databases, usually made in half-automatic mode — at first stage special utility perform analysis of content and detection of site's category. At second stage, collected information often checked manually, that make final decision about site's category. Many companies also collects data about uncategorised sited from the customers.
Currently used two methods of integration with URL databases:
- usage of local URL database, with regular updates. This method is very useful for big companies, that has dedicated filtering servers, that handle big amount of requests;
- usage of remote URL database. This method often used in different hardware-centric solutions — small firewalls, ADSL-modems, etc. Usage of remote database slightly increase network load, but guarantee usage of actual URL database.
Main advantage of using URL databases is, that access rights checked when client send request, and this allow to decrease load of network. But there is also disadvantage — delays in updates of URL databases, as analysis require some time. Some sites also often change their content, and information in URL database become invalid. Some sites also provide different content, based on different parameters — user name, geographic region, time of day, etc.
Online data categorisation
Online site's categorisation also could be performed different ways. Very often used methods, based on statistical approach, but there are also other methods.
One of the simplest approach for data categorisation — usage of Bayes algorithms, that give good account of oneself in fighting with SPAM. But this approach also has some drawbacks — it require periodical re-training and correcting of dictionaries for a new data. Therefore, some companies use more complex methods for detecting site's category during data transfer. For example, the ContentWatch company offer special library, that perform analysis of data, with usage of linguistic information, and can deduce data category, using this information.
Online data categorisation allow to provide a quick response for a new sites, as information about site's category is not dependent on it address, but only content. But this approach has also drawbacks — we need to perform analysis of all transferred data, that could lead to performance degradation. Second disadvantage — need to keep content databases up to date for different languages. Nevertheless, some products use this approach, together with usage of traditional URL databases, for example, Virtual Control Agent in products of SurfControl, and site categorisation methods in SKVT "Dozor-Jet".
Site's category information, provided by sites
Besides usage of URL databases and online data categorisation methods, there is also another approach — site can provide category information. First of all this method intended for home and school users, when parents or teachers could restrict access and/or keep track of sites, that are visited by child. Exists several implementations of this resource categorisation method:
- PICS (Platform for Internet Content Selection) — specification, developed by W3 consortium ten years ago, also having different extensions, aimed to improve reliability of the rating system. For control of the ratings could be used special software, that available from the project's site. More detailed information about PICS you can find at the site of the W3 Consortium.
- ICRA (Internet Content Rating Association) — new initiative, developed by independent
non-commercial organisation with the same name. Main goal of this initiative —
provide protection for childes against access to prohibited content. This organisation
has agreements with many large companies (big telecommunication and software companies)
to make protection more strong.
ICRA provide special software, that allow to check special label, that returned by site, and make decision about providing access to the data on site. This software works only under Microsoft Windows, but, as specification is open, than exists ability to write filtering software also for other platforms. Description of goals and tasks of this organisation you can find on ICRA's site.
Main advantage of this approach — you need only have special software and doesn't need to update URL and/or content databases, as all category information provided by site. But the main drawback is that site could provide false category, and this could lead to restricting access to right site, or providing access to false site. This problem may be resolved (this currently in progress) by using special methods of data integrity checking, such as digital signatures and so on.
Web filtering in world of Web 2.0
Massive introduction of so-called Web 2.0 technologies, made many problems for content filtering. As in many cases, data transferred separately from decoration, exists possibility to skip forbidden data to or from user. When working with such sites, we need to do complex analysis of all transferred data, detecting transmission of additional data, and taking into account the data, collecting in previous transactions.
Currently no companies provide support for complex content filtering for the Web 2.0 sites.
Integration with external systems
In many cases exists need in integration of content filtering systems with some other systems — proxy servers, anti-viruses, etc. In these cases, content filtering systems could act as clients, servers, or both client and servers. For this purpose was developed several standard protocols — Internet Content Adaptation Protocol (ICAP) and Open Pluggable Edge Services (OPES). Besides this, several manufacturers had created their own protocols for providing interoperation with third party software. This is Cisco Web Cache Coordination Protocol (WCCP), Check Point Content Vectoring Protocol (CVP) and some others.
Some protocols — ICAP and OPES, developed with knowledge in mind, that their could be used not only for content filtering, but also for other services — translation services, advertising placement, content adaptation and propagation, based on different policies/rules, and so on.
ICAP
Currently, ICAP is very popular for tasks of integration of content filtering and checking software — anti-viruses and malware detectors, proxy servers, etc. But i should to mention, that ICAP was developed only for work with HTTP, that lead to many restrictions, when we try to adapt it to work with other protocols — SMTP, IM, etc.
ICAP accepted Internet Engineering Task Force (IETF) group as a standard. ICAP described in the RFC 3507 document, with some additions, described in "ICAP Extensions draft" document. These documents available from the site of the project.
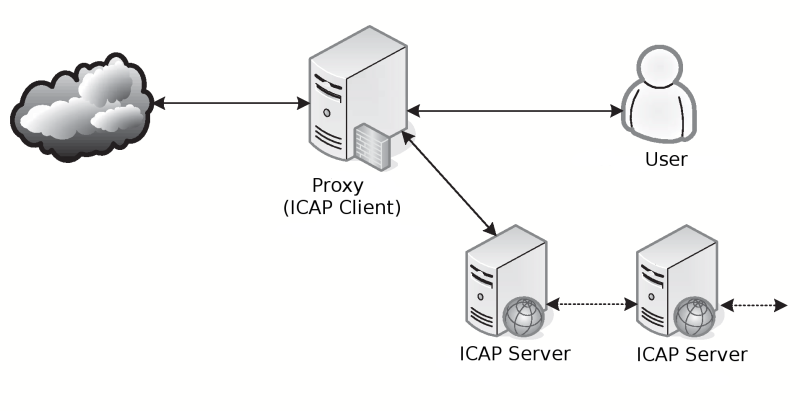
Architecture of the system, that use ICAP you can see on picture above. ICAP Client — is the system, that transfer data. System, that make analysis and processing of data, called ICAP server. ICAP servers could act as ICAP clients for other servers — this allow chaining of the different systems for processing one data flow.
For interoperation between client and server used protocol, that looks like HTTP version 1.1, and use the same methods of information coding. According standard, ICAP can process both outgoing (REQMOD — Request Modification mode), and incoming (RESPMOD — Response Modification mode) data.
Decision about which data will processed is made by ICAP client, and in some cases this is doesn't allow to make full data processing. Client settings, vary in different implementations, and in some cases, we can't change them to allow processing of all transferred data.
After receiving data from client, ICAP server perform their processing, and, if necessary, then modify them. After processing, data returned to the ICAP client, and transferred to the client or server, depending of data transfer direction.
ICAP widely used by manufacturers of malware detection software, as it allow to interoperate with different products uniform way, and not depend on platform, on which run concrete ICAP client.
Main drawbacks of the ICAP usage are:
- additional network operations between clients and servers, add latency during data transfer between external systems and data consumers;
- exists some checks, that we need to run on the client side, not on server side — content type detection and so on. This is very actual, as in many cases, ICAP client use file extension or data type provided in headers, to decide should it pass data to ICAP server or not. Using of wrong extension, for example, may lead to skipping check and violation of security policy;
- very hard integration with system, that process not only HTTP protocol.
OPES
In difference from ICAP, OPES was designed with application for other protocols in mind. It also take into account details of concrete protocols. Besides this, designers of OPES take into account drawbacks of ICAP, such as, absence of authentication between client and server, identity confirmation, and so on.
OPES also accepted as standard by Internet Engineering Task Force. All information about structure of service interoperation, requirements for services, and security solutions described in documents RFC 3752, 3835, 3836, 3837 and some others. This list is regularly updated by new documents, that describe application of OPES not only for HTTP-traffic, but also for SMTP, and some other protocols.
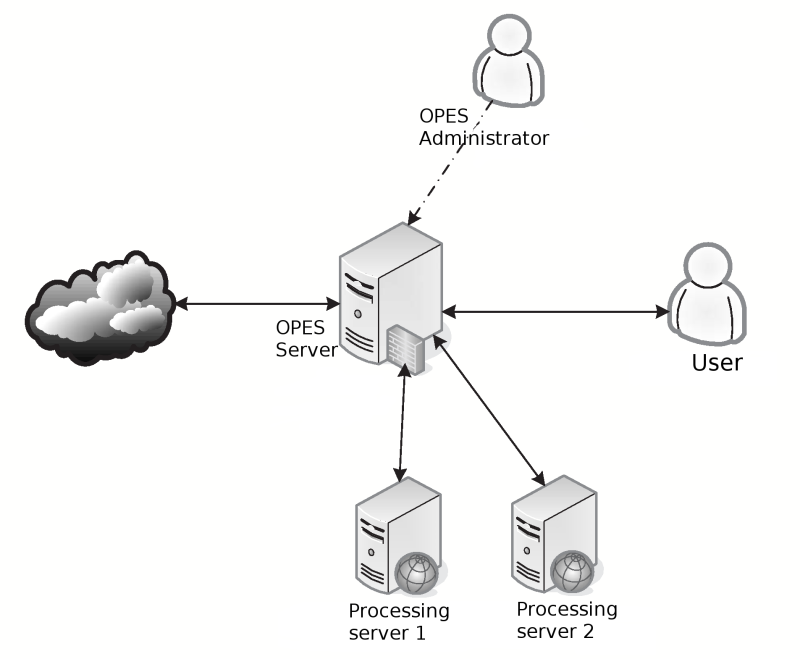
Interoperation between servers and clients of OPES you can see on picture above. In common details, it looks like scheme for ICAP, but exists some important differences:
- exists some requirements to OPES clients, that make working with them more comfortable
— setting filtering policies, access rights, and so on;
- Data consumer (user's information system) can influence on the data processing. For example, if automated translators is used, then transferred data could automatically translated to the user's language;
- Data producers, also can influence on data processing;
- data processing servers during analysis could use protocol-specific data, that their used for data transfer;
- some data processing servers, could get more important data if they stay in friendship with OPES client, data consumers and/or data producers.
All features, listed above, depends only on configuration, that was used during system installation. This makes OPES usage more comfortable and perspective, than usage of ICAP.
In near future is awaiting products, that will support OPES, together with ICAP. Pioneer in this branch is Secure Computing Corp. with their product line called Webwasher.
As currently no complete implementations of OPES, than we couldn't make conclusions about drawbacks or advantages of this approach, but theoretically exists only one drawback — increasing of latency due interoperation between OPES clients and servers, same as in ICAP.
HTTPS and other kinds of encrypted traffic
Some experts give information, that up to 50% of Internet traffic transferred in encrypted form. Controlling of such traffic is very actual for many organizations, as some users may use encryption for creating a data leakage channels. Besides this, encrypted channels also could be used by malicious code.
Exists several tasks associated with processing of encrypted traffic:
- analysis of data, transferred via encrypted channels;
- checking of certificates, that used by servers for creation of encrypted channels.
Control of encrypted data transfer
Control of data, that transferred over encrypted channels, is most important task for companies, which employers has access to Internet. For implementation of such control, used approach called "Man-in-the-Middle" (in some sources it also called "Main-in-the Middle"), that also could be used by crackers for data interception. Scheme of encrypted data processing you can see on picture below.
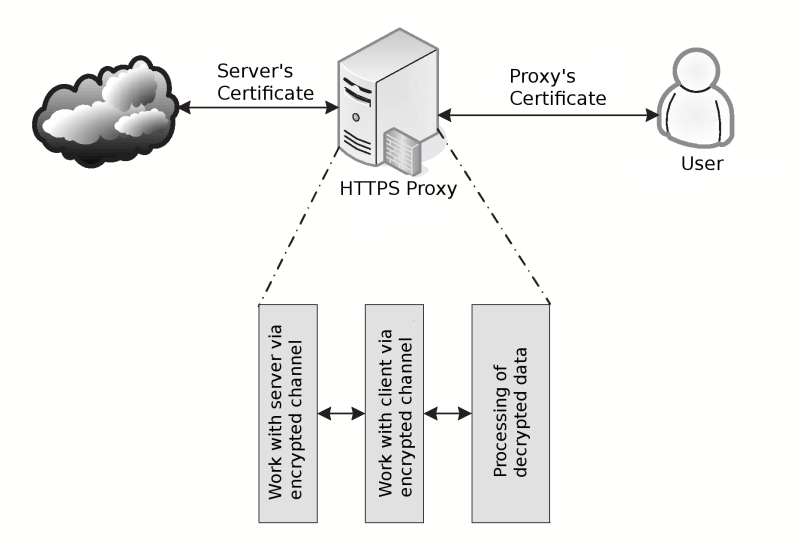
Processing of encrypted data include following steps:
- In the user's Internet browser installed special certificate, that will used by proxy-server for signing generated certificates (without installing this certificate, browser will complain about using certificate from non-trusted authority);
- during handshake with proxy server, client got dynamically generated certificate, filled with details of destination server, but signed with our own key — this allow proxy-server to decrypt transferred data;
- decrypted data analyzed like a normal HTTP-traffic;
- proxy-server set up connection to destination server, and use server's certificate for data encryption;
- data, that proxy get from the destination server, decrypted, analyzed and encrypted with generated certificate before sending them to client.
When this scheme of encrypted data processing is used, there is some problems, related to confirmation of user's identity. Also, we need to do some jobs for installing generated certificates into the user's browsers.
Now there are several products implement processing of encrypted data: Webwasher SSL Scanner by Secure Computing, Breach View SSL, WebCleaner.
Certificates checking
Second task, related to the usage of encrypted channels — checking validity of certificates, used by servers.
Some peoples could make attacks against IT-infrastructure by creating a fake record in DNS, that will point to the fake site, instead of original. By using such sites, could steal important user's data, such as credit card's numbers, passwords, and so on. Also such sites, could provide a malicious code, masked for critical updates, etc.
To preventing such attacks, exists special software, that check validity of certificates, used by servers for creation of encrypted channels. When provided data not match the server's data, or certificate doesn't signed by trusted authority, then system could block access to these sites, or ask user before providing access to them. Scheme of data processing is almost same, as in first task, but analyzed only data from server's certificate.
E-Mail filtering
When organizations use e-mail, they need to implement protection for incoming and outgoing traffic. But, for each direction we need to solve different tasks — for incoming traffic we need to implement protection against malware, SPAM & phishing, but for outgoing traffic we need to take control over contents of outgoing documents — preventing information leakage, etc.
Most of the existing products provide control only for incoming traffic. This usually made via integration with anti-virus systems, implementing different approaches to detect SPAM and phishing. Some of these functions often integrated into e-mail clients. For protecting users from SPAM, currently used different methods:
- comparison of incoming mail with existing database of SPAM messages. For comparison could be used different methods, like a genetic algorithms, as spamers try to mask their messages by replacing letters in words by numbers and vice verse;
- dynamic categorization of messages by their content. This method is very effective for detecting SPAM messages. For make this method impossible, spamers send text as a pictures, and/or add word corpus not belonging to the SPAM messages. Usage of these methods make dynamic categorization less precise. But now, some manufacturers of anti-spam solutions start to introduce new methods, like a wavelet analysis and/or OCR;
- gray, white & black access lists allow to describe rules of mail receiving from well-known or unknown sites. Usage of gray lists could stop SPAM messages, due existing of some peculiar features of SPAM sending software. For black list could be used and local databases, controlled by e-mail administrator, and global lists, that updated by external users. But usage of global black lists could be dangerous, as they also can contain big networks with "good" severs.
For preventing data leakage could be used different methods, based on interception of e-mail messages and performing deep analysis of them according complex security policies. In this case we need to perform precise detection of content types, languages and encodings, performing semantic analysis of the texts.
E-mail filtering systems could also used for task of creating encrypted e-mail streams, when system automatically encrypt outgoing message, and check and decrypt incoming. This is very useful, when you want to control all e-mails, but their should be encrypted when transferred via public channels.
Filtering of instant messaging
Tools for instant messaging become a very popular instrument in many companies. They provide quick exchange of messages between employees and/or clients of company. This lead to creation of tools, that control exchange of instant messages, and could prevent information leakage and malware propagation.
Now most popular instant messaging products (and corresponding protocols) are MSN (Microsoft Network), ICQ, AIM (AOL Instant Messaging), Yahoo! Chat, Jabber and their corporate analogs — Microsoft Live Communication Server (LCS), IBM SameTime and Yahoo Corporate Messaging Server. All these products provide almost same functionality — sending of messages (both via central server, and direct from user to user) and files. Now, almost all products also support transmission of voice and video between computers. For filtering systems this lead to requirement of VoIP analysis.
Usually, products for control of instant messaging implemented as application level gateway, that perform analysis of data, and blocking inappropriate traffic. But there is also implementations, that use application servers extended with content filtering features. For filtering of instant messaging following functions of filtering products are most important:
- controlling usage of certain protocols;
- control names and versions of used clients;
- providing access only for certain users;
- allow to contact only with users inside company and/or only with certain users outside company;
- checking of transferred texts;
- checking of transferred files for size and content types;
- setting different policies for different directions of data transfer;
- checking for malware;
- SPIM detection;
- saving of transferred data for additional checks and archiving.
Now exists following products for content filtering of instant messaging (not all, but most well known):
- CipherTrust IronIM by Secure Computing. This product support AIM, MSN, Yahoo! Chat, Microsoft LCS and IBM SameTime protocols. Now this is one of the most powerful products;
- IM Manager by Symantec (was developed by IMLogic, that was acquired by Symantec). This product provide analysis of Microsoft LCS, AIM, MSN, IBM SameTime, ICQ and Yahoo! Chat protocols;
- Antigen for Instant Messaging from Microsoft also allow to analyse almost all popular instant messaging protocols.
Products of other companies (ScanSafe, ContentKeeper) has less features comparing with products, listed above. I need also to mention two Russian companies — "Gran Pri" (with product "SL-ICQ") and "Mera.ru" (with product "Sormovich"), that has products for filtering of instant messages transferred with ICQ protocol.
VoIP filtering
Voice over IP (VoIP) systems also become very popular (one of the first implementations — Skype has big amount of users). Users could send voice not only between computers, but also use these systems to make calls to usual phones. This lead to need of the systems, that will provide control of such traffic.
Exists standardized, open protocols for VoIP, for example, Session Instantiation Protocol (SIP), created by IETF, and H.323, developed by ITU. For these protocols, creation of controlling software is possible, as exists their description. But also exists, closed, non-documented protocols, that make their processing almost impossible.
All existing now products we could divide on two categories:
- products, that can detect and block VoIP-traffic;
- products, that can detect, intercept and analyze VoIP-traffic.
To first category belongs following products:
- Products of "Dolphian" company allow to detect and allow or block VoIP-traffic (SIP and Skype), that encapsulated into standard HTTP;
- products of Verso Technologies;
- some firewalls also has such function.
To second category belongs:
- products of Russian company "Sormovich" support interception, analysis and storing of voice information, transferred with H.323 and SIP;
- open source library Oreka allow to detect signal part of voice traffic and capture this data, to following analysis with help of other tools.
Not so much time ago was announced, that ERA IT Solutions AG company had developed product, that can capture and analyze protocol used by Skype. But for it use, it's necessary to install specialized client on computer where Skype installed.
Peer-to-peer filtering
Usage of peer-to-peer (p2p) networks make them very dangerous for organizations due following possible threats:
- propagation of malicious code;
- information leakage;
- distribution of copyrighted data could lead to legal abuse of company;
- increasing load of data channels.
Exists big number of networks, that use peer-to-peer for data transfer. Some of them use schemes with central servers, that coordinate users, but some of them are fully distributed, without one coordinators. Second case — is worst for filtering software manufacturers. For controlling and processing of p2p-traffic exists following solutions:
- SurfControl Instant Messaging Filter, that process p2p together with instant messaging;
- Websense Enterprise also provide detection and blocking of peer-to-peer traffic;
- Webwasher Instant Message Filter allow to control user's access to different peer-to-peer networks.
Usage of these, or other products could significantly decrease risks from usage of peer-to-peer networks.
Unified Threat Management
Many companies provides solutions, build according the Unified Threat Management strategy. Usually, such products built on the base of different firewalls, that besides their main functions, also provide content filtering functions. Usually, their provide intrusion detection & prevention functions, together with functions of malware detection.
Many of these products implemented as appliances, and can not replace specialized content filtering products, as these appliances can not check all specific things, well known for specialized solutions. Usually such solutions used for avoiding duplication of functionality in different products, and make sure, that all protocols handlers use same threat database.
Most popular products, implementing Unified Threat Management concept are:
- SonicWall Gateway Anti-Virus, Anti-Spyware and Intrusion Prevention Service provide anti-virus check of data, transferred with SMTP, POP3, IMAP, HTTP, FTP and NetBIOS protocols, some of Instant Messaging, audio- and video-streaming protocols;
- Appliances ISS Proventia Network Multi-Function Security, provide blocking of malware and SPAM/SPIM, and also intrusion prevention. Appliance supplied with many checks, that could be extended by user;
- Network Gateway Security appliances produced by Secure Computing, besides protection from malware and unwanted messages, also has VPN support. Theseappliances include almost all products from Secure Computing.
There are many other solutions, but listed above are most widely used.
Lawful interception
Lawful interception was used government security agencies for a long time. But in last years, problems of interception and analysis different kinds of traffic (not only Internet, but also voice from usual phones, etc) become very actual. Even, that countries, that resist against these systems, now start to introduce them for controlling data transfer. As such systems should intercept different kinds of data, transferred via high speed channels, we need to have dedicated intercept modules, and dedicated software for analysis of collected data.
As most well-known system i should mention "Echelon" system, that used by special agencies of USA and United Kingdom for collecting data's for intelligence services. Besides this, US agency of national security use "Narus" system, that allow monitoring, interception and analysis of Internet traffic in real-time.
Among Russian companies i should mention "Sormovich" company, manufacturer of products, that allow to intercept, analyse and store e-mail, voice and other kinds of traffic (HTTP and other).
Conclusion
Evolution of IT systems also lead to appearance of new threats. So, development of content filtering, and other kinds of security-related products, not only try to keep track of these threats, but also try to prevent new threats, decreasing risks for information systems.
1. This article, was originally published in October 2006 at JetInfo Magazine in Russian language. Current version, was changed to correspond current things. Except this, also was deleted a section about products of Jet Infosystems, description of that you can find at their site.
2. English is not my native language, so if you have remarks and suggestions for improvement this article, please write me by mail - alexott@gmail.com
Last change: 05.03.2013 16:54
