Меню:
The PSVN package provide same functionality for Subversion, as the PCL-CVS for CVS. This package provide user access to all features of Subversion.
Installation of package
Installation of package is pretty simple — download latest version from site, put it to place, where Emacs can find it, and add following line to initialization file:
(require 'psvn)
Work with package
The PSVN package use almost same principles as the PCL-CVS package — all work is
performed in special buffer. Currently this buffer is created only by svn-status
function. Buffer, that created by svn-status function has name *svn-status*. Example of
this buffer, you can see on the picture below.
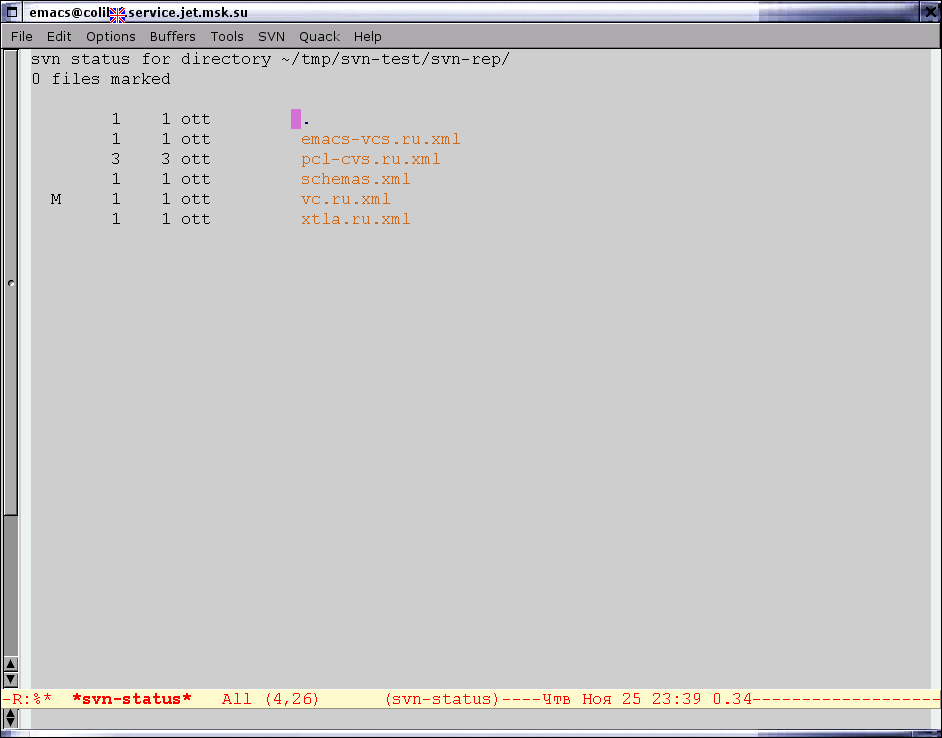
As you can see on picture, information is displayed as a table. In first column the
status of object is displayed. In second column — version number for given object, in
the third — number of version, when file was changed, in the fourth column — name of
user, who had changed this object, and in the last column — object's name. List of
available statuses and their descriptions you can find in the output of svn status -v
command.
Functions, that are performed by user is applied to current file, or to marked files. User
can execute functions using key bindings, or using menu, called SVN, that displayed in the
*svn-status* buffer.
Navigation and work with marks
User can navigate in *svn-status* buffer with almost same functions as in packages for
other VCS — he can use either arrow keys, either functions: svn-status-previous-line
(bound to C-p) to move to previous line, and svn-status-next-line (bound to C-n) to move
to the next line. This is slightly different from other packages, that use n and p for
these actions.
To set marks to objects PSVN use same key bindings as other packages — to mark object the
m key (svn-status-set-user-mark) is used, and to remove mark the u key
(svn-status-unset-user-mark) is used. Besides this, to remove all marks, user can use the
svn-status-unset-all-usermarks function (M-DEL or * ! key bindings), and to remove a mark
from an object, that located before cursor, user can use
svn-status-unset-user-mark-backwards function, that bound to DEL key.
User can also mark files with concrete status. To mark modified files user can use
svn-status-mark-modified function (* M), to mark added files —
svn-status-mark-added
function (* A), and to mark not registered files —
svn-status-mark-unknown function (* ?).
Work with files
User can add files to repository using several functions. Most often used function is
svn-status-add-file (it bound to a), that add file(s) (current one or several marked) to
repository. There are also svn-status-add-file-recursively function (A key), that add
files recursively, and svn-status-make-directory function (+ key), that creates directory
in repository. Don't forget, that addition of files is performed only in your directory,
and files will added to repository only after explicit commit.
Deletion of files is performed with svn-status-rm function (D key or C-d), that executes
svn rm command. As Subversion supports renaming of files with preserving of history, and
PSVN also has function to perform this operation. This function is called svn-status-mv
and bound to R key. User also must explicitly commit its changes to repository.
You can use update your work directory from repository with svn-status-update-cmd function
(U key), that executes svn update command. You can also fetch concrete version of file
with svn-status-get-specific-revision function (~ key). After execution of this command,
file with name F.~REVISION~ will created, and it will contain data for concrete version.
You can obtain state of parent directory with the svn-status-examine-parent function, that
bound to ^ key.
You can view and edit files directly from *svn-status* buffer. To open file in the same
windows as *svn-status* buffer you can use svn-status-find-files function (f key). And to
open file in other window, you can use svn-status-find-file-other-window function (o key).
You can also view file with svn-status-view-file-other-window function (v key), that is
very handy when you don't want to change file. The RET key
(svn-status-find-file-or-examine-directory) performs two operations — it either opens
file, or displays state of files in given directory.
Work with changes
As was mentioned above, after performing almost all operations you need explicitly commit
changes to repository. You can do this with svn-status-commit-file function (c key).
After you perform this operation, your changes will available to all users, who are
working with this repository.
You can also remove changes, that you did in files. This operation is performed with
svn-status-revert function, that bound to r key. Subversion supports removing of conflict
state from files, that has this status. To do this, you can use svn-status-resolved
function (V key), that executes svn resolved command.
As in many other packages that works with VCS, PSVN implements functions that allow to get
list of changes in files between current and base versions. The svn-status-show-svn-diff
function (= key), displays differences between modified file and its version
in repository. The svn-status-show-svn-diff-for-marked-files function (C-=)
performs this operation for all marked files. And the svn-status-ediff-with-revision
function (E key) uses Ediff to perform this operation. All these functions support
comparison with arbitrary version, if they'll get prefix argument before they execution.
Work with metadata (properties)
Subversion allows users to add metadata (properties) to the files and concrete versions.
Changes in metadata is propagated together with other changes, introduced in files. More
detailed information about metadata you can find at Version Control with Subversion book.
The PSVN package provides number of functions to work with metadata. These commands
accessible via direct call of functions, and also via key bindings. The P key is used as
a prefix key for all these key bindings.
All available functions we can split into two groups: first one is used for work with any metadata, and second — to work with concrete properties.
The first group includes following functions:
svn-status-property-parsefunction (P p) is used to parse metadata recordsvn-status-property-set(P s) is used to set value to concrete propertysvn-status-property-delete(P d) removes selected propertysvn-status-property-listfunction (P l) displays list of properties, defined for given objectsvn-status-property-edit-one-entry(P e) allows user to change metadata interactively.
Into second group are included following functions:
svn-status-property-edit-svn-ignore(P TAB) allows user to edit list of files, ignored by Subversionsvn-status-property-ignore-file(P i) put current file (or marked files) into list of ignored objectssvn-status-property-ignore-file-extension(P I) add regular expression to list of ignored files, that allows to ignore all files with same extensions as for current filesvn-status-property-set-eol-style(P y) set 'end of line' style for given objectssvn-status-property-set-keyword-list(P k) allows to edit keywords list for given objects
Information retrieving and other functions
To get information about current object user can use svn-status-info function, that bound
to i key. After its execution, buffer called *svn-process* will contain result of
execution of svn info command. If this information could contain too many details, then
user can use svn-status-parse-info function (I key), that analyze this information and
makes it more compact. To get information about author and version of file, user can use
svn-status-blame function (b key), and to view log for selected files, there is
svn-status-show-svn-log function (l key).
To update content of *svn-status* buffer you can use svn-status-update function (g key).
To see output of svn process you can press s key (svn-status-show-process-buffer).
You can also control, which files will displayed in the *svn-status* buffer (by default
all files are shown). To hide not modified files the svn-status-toggle-hide-unmodified
function (_ key) could be used, and to hide all unknown files exists
svn-status-toggle-hide-unknown function (? key). Both these commands works like switches,
and could be used to switch between displaying and hiding.
To leave the *svn-status* buffer, and kill it you can use svn-status-bury-buffer function,
that bound to q key.
Customization
User can change behaviour of package using standard Emacs customization routines.
Corresponding customization groups is called psvn. PSVN also use several hooks, that
could be used to customize parameters of new buffers, or functions. The
svn-log-edit-mode-hook hook is called when some buffer enters into svn-log-edit mode, and
svn-log-view-mode-hook is called, when buffer enters into svn-log-view mode.
Last change: 05.03.2013 16:54
